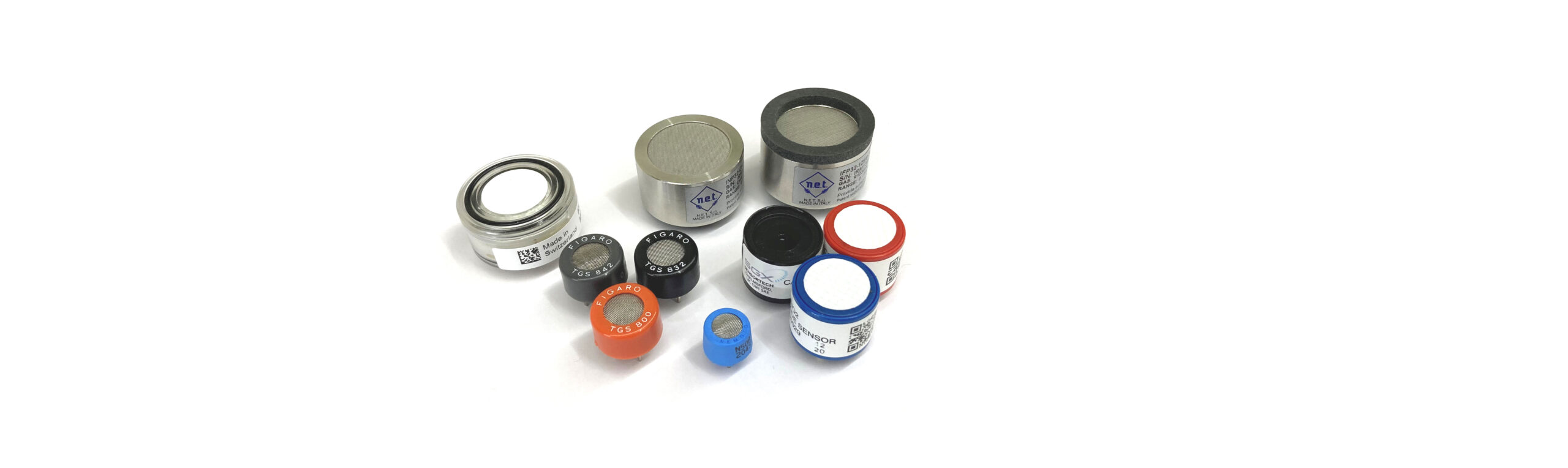
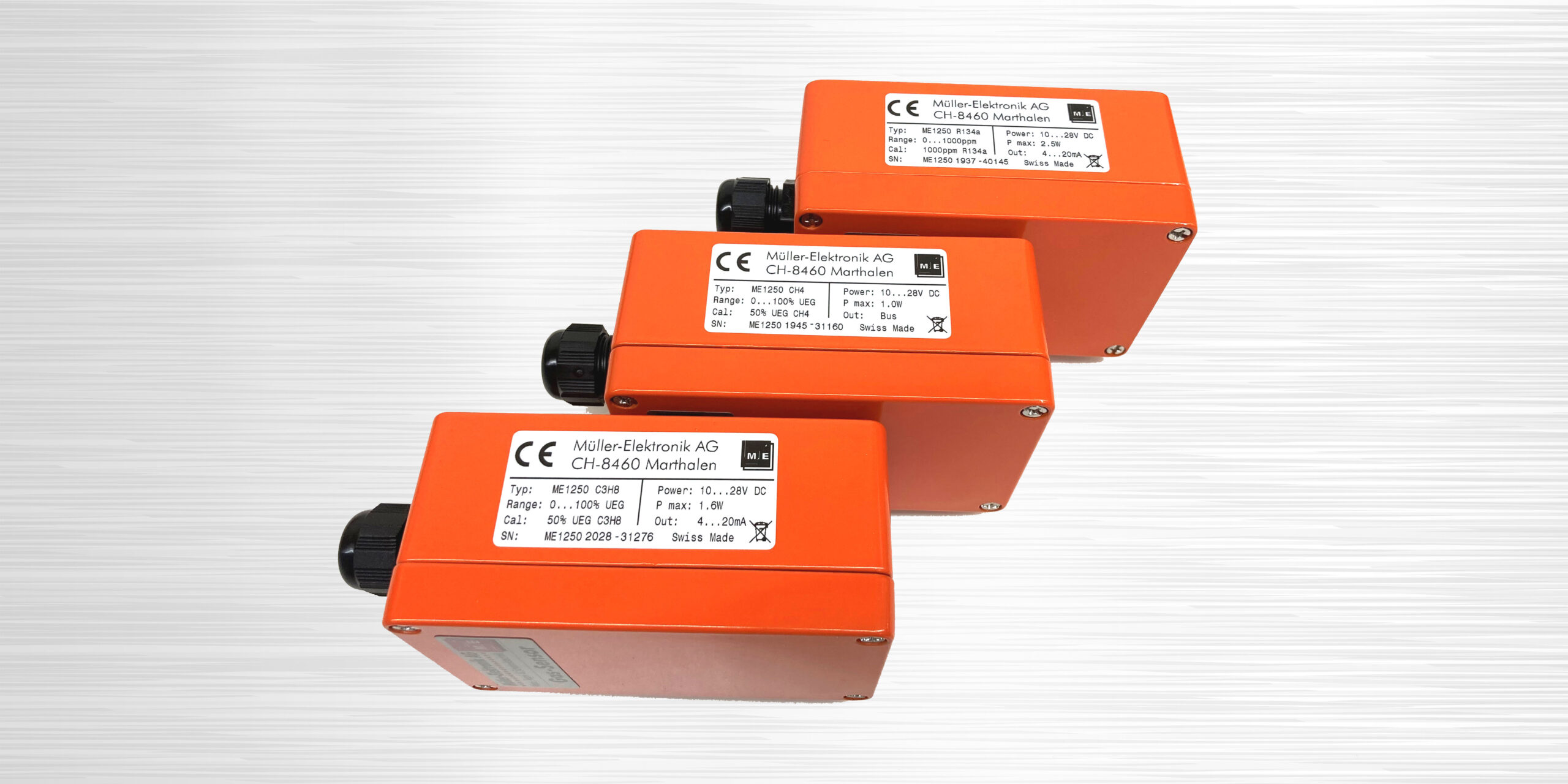
In order to ensure safe and reliable detection of flammable and/or toxic gases, the correct selection of the appropriate gas sensor is of crucial importance. This page describes the basics, the different types of gas sensors, and how to use them.
There are around 200 to 300 different gases. Every gas has its own properties. It should be mentioned that certain gases do not appear to be dangerous or even flammable gases at first glance. However, depending on the application, detection is desirable or even mandatory.
Let’s take the harmless gas oxygen (chemical formula O2) as an example. It occurs in the natural atmosphere at 20.9% by volume and is vital for humans and animals. However, if the proportion of oxygen is reduced, it can become life-threatening. Likewise vice versa if the proportion of oxygen is increased. With an increased oxygen concentration (more than 25% by volume), the flammability of materials is changed unfavorably, even to the point of self-ignition. With a reduced oxygen concentration of less than 17% by volume, one speaks of oxygen deficiency, which already includes the danger of unconsciousness through to suffocation. An initially harmless gas with significant effects.
In the case of toxic, i.e. poisonous, gases, there is a risk of serious injury or poisoning. It is important not to exceed the workplace maximum exposure. The exposure over time is also to be considered for the occupational health of personnel. Humans do not have any sensory organs that warn or even protect them from excessive concentrations. The monitoring must be carried out by a gas sensor that is suitable for the gas compound in question.
The situation with combustible gases is similar to that with toxic (poisonous) gases. Combustible gases can be ignited in a certain ratio based on the oxygen concentration. Here, too, a human has no sensory organ that warns or protects from gas exposure. The monitoring must be carried out by a gas sensor that is suitable for the gas compound in question.
In general, a distinction is made between 4 different gas sensors and their detection principle.
Electrochemical

In the electrochemical measurement of a gas sensor, toxic (poisonous) gases and/or vapors as well as the oxygen concentration (deficiency or excess) are detected. These gas sensors are further characterized by the following features:
- Gas sensor has a high sensitivity
- Gas sensor has a very high selectivity
- Gas sensor has a short service life (usually only a maximum of 2 years)
- Gas sensor is hardly susceptible to poisoning
Catalytic / Heat-of-reaction principle / Pellistor
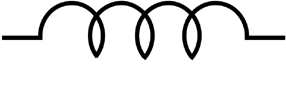
The gas sensor contains a measuring cell called a pellistor. The gas sensor with the pellistor is only used for the detection of combustible gases and vapours. These gas sensors are further characterized by the following features:
- Gas sensor is very inexpensive
- Gas sensor has a long service life (usually up to 5 years)
- Gas sensor is susceptible to poisoning, e.g. by silicone compounds
Semiconductor
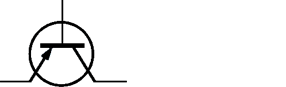
Semiconductor gas sensors are used to detect combustible and toxic (poisonous) gases and vapors. These gas sensors are further characterized by the following features:
- Gas sensor is very inexpensive
- Gas sensor has a high cross-sensitivity to other gases
- Gas sensor has a long service life (usually approx. 3 years)
Infrared

Infrared gas sensors are used to detect combustible gases and vapors. The greatest advantages of these gas sensors include the very high selectivity and the very long service life. Selectivity means that a gas sensor which is designed for a specific gas, only this gas is detected and the device is insensitive towards other gases. These gas sensors are further characterized by the following features:
- Gas sensor is not susceptible to poisoning
- Gas sensor is failsafe
- Gas sensor does not require an oxygen atmosphere